If You Spit Up Blood in Rhe Morning and Never Again Should You See a Doctor
Blood in the sputum or fungus when a person coughs or spits is called hemoptysis. Although the claret tin be worrying, it is usually not a cause for concern, peculiarly in young or otherwise healthy people.
Blood in the sputum is a
It tin be alarming to cough upwards a pregnant corporeality of blood in sputum or to see blood in mucus frequently. In severe cases, this can result from a lung or stomach condition.
In this article, we talk over the causes and treatments of claret in sputum.
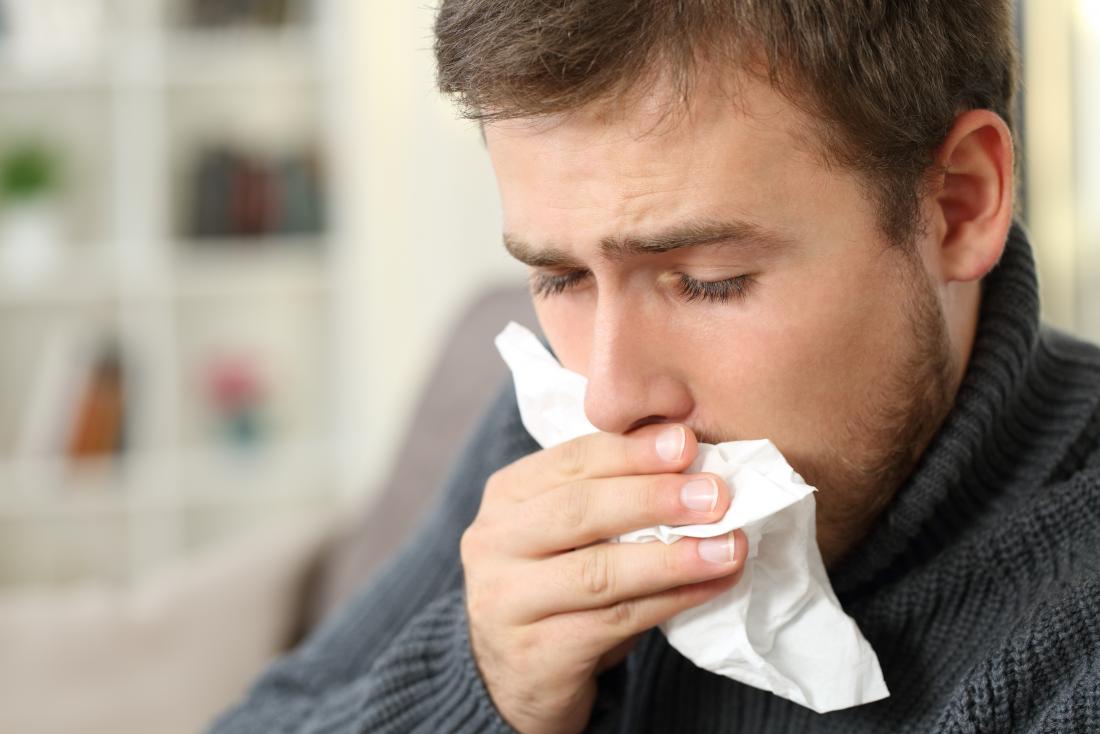

Claret in the sputum usually comes from the lungs, merely information technology tin also come from the breadbasket or digestive tract.
A range of factors can lead to blood in the sputum. Likewise, the claret may originate from unlike parts of the body.
The blood usually comes from the lungs, but less ofttimes it can come from the stomach or digestive tract. If the claret comes from the digestive tract, the medical term is hematemesis.
- From the lungs (hemoptysis). If the blood is bright red, frothy, and sometimes mixed with mucus, it probably comes from the lungs and tin result from persistent cough or a lung infection.
- From the digestive tract (hematemesis). If the claret is nighttime and comes with traces of food, it probably originated in the stomach or elsewhere in the digestive tract. This may be a sign of a more serious condition.
Possible causes of blood in the sputum include:
- Bronchitis. Chronic bronchitis is oft behind the appearance of claret. The condition involves persistent or recurring inflammation of the airways, forth with a cough and the production of sputum.
- Bronchiectasis. This describes a permanent enlargement of parts of the lungs' airways. It oft occurs with an infection, shortness of breath, and wheezing.
- A prolonged or severe cough. This tin irritate the upper respiratory tract and tear the blood vessels.
- A severe nosebleed. Many factors tin cause nosebleeds.
- Drug use. Drugs, such equally cocaine, that are inhaled through the nostrils can irritate the upper respiratory tract.
- Anticoagulants. These medications forestall the blood from clotting. Examples include warfarin, rivaroxaban, dabigatran, and apixaban.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). COPD is a permanent obstruction of airflow from the lungs. Information technology usually causes difficulty breathing, a cough, the production of sputum, and wheezing.
- Pneumonia. This and other lung infections can cause bloody sputum. Pneumonia is characterized by inflammation of the lung tissue, commonly considering of a bacterial infection. People with pneumonia tend to have chest pain when breathing or coughing, fatigue, fever, sweating, and chills. Older adults can also experience confusion.
- Pulmonary embolism. This refers to a blood clot in one artery of a lung. It normally causes chest pain and sudden shortness of breath.
- Pulmonary edema. This describes fluid in the lungs. Pulmonary edema is most common in people with heart weather. It causes pink and frothy sputum, too equally severe shortness of breath, sometimes with chest pain.
- Lung cancer. A person is more likely to have lung cancer if they are older than forty and smoke tobacco. It tin can crusade a coughing that does not go away, shortness of breath, chest hurting, and sometimes os hurting or headaches.
- Neck cancer. This usually starts in the throat, larynx, or windpipe. It tin can cause a swelling or sore that does non heal, a permanent sore throat, and a carmine or white patch in the rima oris.
- Cystic fibrosis. This inherited status severely damages the lungs. It ordinarily causes difficulty animate and a persistent coughing with thick fungus.
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis. This describes inflammation of the blood vessels in the sinuses, lungs, and kidneys. It ordinarily causes a runny nose, nosebleeds, shortness of breath, wheezing, and a fever.
- Tuberculosis. A leaner causes this severe lung infection, which can lead to a fever, sweating, breast pain, pain while breathing or coughing, and a persistent cough.
- Narrowed heart valves. A narrowing of the heart's mitral valve, called mitral valve stenosis, can cause shortness of jiff, specially with exertion or when lying down. Other symptoms include swollen anxiety or legs and heart palpitations or fatigue, peculiarly with increased physical activeness.
- A serious injury. Trauma to the chest can cause claret to appear in the sputum.
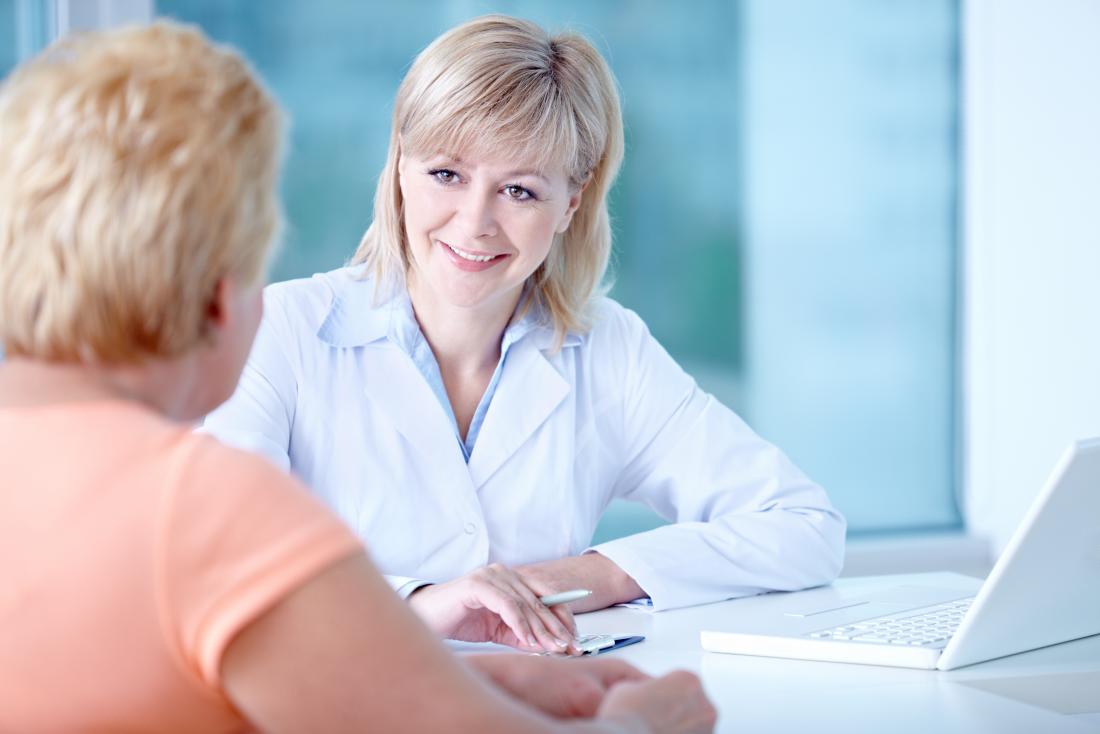

A person who is coughing blood in large amounts, or at frequent intervals, should visit a medico.
See a doc or seek emergency care when coughing brings upwardly a lot of claret, or whatever blood at frequent intervals.
If the blood is dark and appears with pieces of food, go to a hospital immediately. This can indicate a severe problem originating in the digestive tract.
Also, see a doctor if whatsoever of the following symptoms back-trail blood in the sputum:
- a loss of ambition
- unexplained weight loss
- claret in the urine or stools
- chest pain, dizziness, fever, or light-headedness
- worsening shortness of breath
To determine whether a medical condition is causing blood to appear in the sputum, a medico will commonly take a medical history and perform a physical examination.
During the examination, the md may ask the person to cough, and they may check the nose and oral fissure for sites of haemorrhage. The doctor may also take samples of sputum and blood for testing.
In some cases, boosted examinations are necessary. These may include a chest X-ray, a CT scan, or a bronchoscopy, which involves a camera at the end of a tube being inserted into the airway.
Steroids may assist if an inflammatory condition is causing the haemorrhage.
Treatments aim to stop the bleeding and treat the underlying crusade.
Possible treatments include:
- Steroids. Steroids can assist when an inflammatory condition is behind the bleeding.
- Antibiotics. Antibiotics are used in cases of pneumonia or tuberculosis.
- A bronchoscopy. This provides a shut await at possible sources of bleeding. An instrument called an endoscope is inserted into the airways through the olfactory organ or mouth. Tools can exist attached to the stop. Some are designed to stop bleeding, while others, for example, tin can remove a blood clot.
- Embolization. If a major blood vessel is responsible for claret in the sputum, a doctor may recommend a procedure called embolization. A catheter is passed into the vessel, the source of the haemorrhage is identified, and a metal coil, chemical, or fragment of gelatin sponge is used to seal it off.
- Blood production transfusion. A transfusion of elements in the blood, such as plasma, clotting factors, or platelets, may be required if clotting problems or excessively thin blood are responsible for the appearance of blood in sputum.
- Chemotherapy or radiotherapy. These may be used to treat lung cancer.
- Surgery. This may be required to remove a damaged or malignant portion of the lung. Surgery is commonly considered a last resort and simply an selection when bleeding is severe or persistent.
Blood in sputum, particularly in modest quantities, is unremarkably not a cause for concern. Notwithstanding, in people with a medical history of respiratory bug or who smoke, it often requires further evaluation.
Respiratory infections, other lung conditions, and less ordinarily problems in the digestive tract can crusade the blood to appear. Some causes are mild and resolve on their own. In other cases, medical intervention is necessary.
If a coughs upwards claret in large amounts or at frequent intervals, they should encounter a dr..
Read the commodity in Spanish.
crothersnuied1997.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321563#:~:text=Respiratory%20infections%2C%20other%20lung%20conditions,they%20should%20see%20a%20doctor.
0 Response to "If You Spit Up Blood in Rhe Morning and Never Again Should You See a Doctor"
Postar um comentário